A Complete Guide to Refinancing Your Auto Loan

If you’re looking for ways to reduce your monthly expenses or pay less interest on your car, refinancing your auto loan may be a smart financial move. Many drivers don’t realize they can replace their current car loan with a new one that offers better terms, potentially saving hundreds or even thousands of dollars over the life of the loan.
This guide explains what refinancing is, when it makes sense, and how to go through the process step by step.
What Is Auto Loan Refinancing?
Auto loan refinancing is the process of replacing your current car loan with a new one, typically from a different lender, but sometimes from the same one. The new lender pays off your existing loan, and then you begin making payments on the new loan.
You’re not changing cars; the vehicle stays the same. What changes is the loan agreement: things like your interest rate, monthly payment amount, and length of repayment.
Why would someone refinance?
People typically refinance to:
- Lower their interest rate
- Reduce their monthly payment
- Pay off the vehicle faster
- Remove or add a co-signer
- Switch to a lender with better service or benefits
A simple example
If you originally financed your car when rates were higher or your credit score was lower, you may be paying more interest than necessary. Refinancing at a lower rate means you keep the same car but potentially pay less over time.
When Does Refinancing Make Sense?
Refinancing is not always the best option, but it can be beneficial in several situations:
Your credit score has improved
If your score has increased since you bought the car, lenders may now offer you a lower rate.
Market interest rates have dropped
Auto loan rates change with the economy. When rates decrease, refinancing can help you take advantage.
You want to lower your monthly payments
Refinancing to a longer loan term can reduce your payment and create extra room in your budget.
You want to pay off your loan sooner
Refinancing to a shorter term can reduce total interest paid and help you own your car faster.
You want to remove a co-signer
If you no longer need a co-signer (or need to add one), refinancing can change the borrower structure.
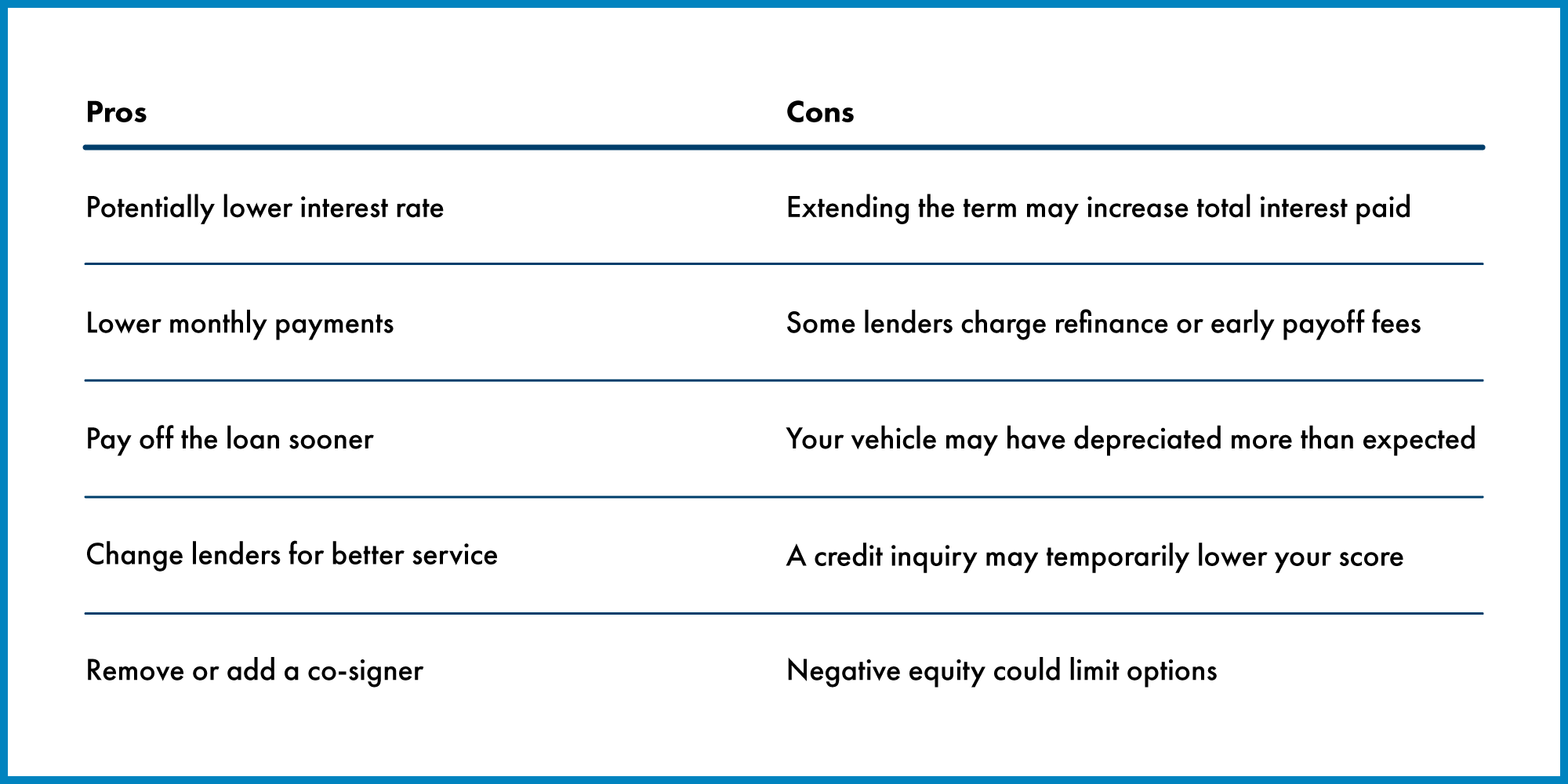
Pros and Cons of Refinancing
How to Refinance Your Auto Loan: Step-by-Step
Refinancing is usually simple and can often be completed in a few days.
1) Review your current loan
Gather details including:
- Remaining balance
- Monthly payment
- Current interest rate
- Payoff amount
2) Check your credit score
Higher scores generally qualify for better rates.
3) Estimate your vehicle’s value
Lenders want to know the car is worth at least close to what you owe. Sites like Kelley Blue Book or Edmunds can help estimate your car’s value.
4) Compare rates and terms from lenders
Pay attention to:
- APR (Annual Percentage Rate)
- Loan term length
- Monthly payment amount
- Fees (if any)
5) Apply for the refinance loan
Typical documents include:
- Driver’s license
- Proof of insurance
- Income verification
- Vehicle information (VIN, mileage, model year)
6) Your old loan is paid off and replaced
Once approved, your new lender pays off your original loan, and you begin payments under your new agreement.
Example: How Much Could You Save?
Original loan:
- $25,000 balance
- 8.5% APR
- 60 months
After one year, you refinance at:
- $21,000 remaining balance
- 5.25% APR
- 48 months
Depending on your terms, refinancing could save you hundreds of dollars in interest and possibly reduce your monthly payment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does refinancing hurt my credit?
A small temporary dip may happen due to a credit check, but long-term on-time payments may improve your credit.
Can I refinance if I owe more than my car is worth?
You may still qualify, but lenders might adjust your loan terms or require cash to cover the difference.
Is refinancing the same as trading in my car?
No. Refinancing keeps the same vehicle. Only the loan terms change.
Final Thoughts: Is Refinancing Right for You?
Refinancing your auto loan can be a smart financial decision, especially if interest rates have dropped, your credit has improved, or you want lower monthly payments. By comparing lenders and understanding the full terms of your new loan, you can make a choice that benefits your long-term financial goals.
Explore Auto Loan Options at First South Financial
If refinancing sounds right for you, we offer competitive rates, flexible terms, and fast approvals designed to help you save.
View all auto loan options:
https://www.firstsouth.com/auto-loans
Check out our current auto loan specials:
https://www.firstsouth.com/loans/auto-loans/auto-loan-specials
Whether you're refinancing or purchasing, First South Financial is here to help you drive forward with confidence.
« Return to "Blog"






